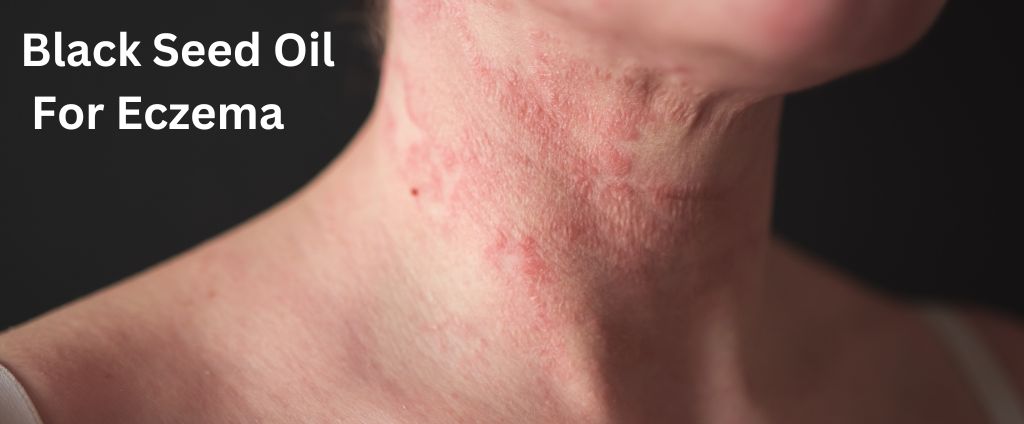
Eczema, a group of skin conditions characterised by red, itchy rashes, is a common issue affecting over 1.5 million individuals in the UK. The most common variant, atopic eczema, impacts 1 in 5 children and 1 in 10 adults. This condition can significantly affect one’s quality of life, leading to physical discomfort and psychological distress. However, the good news is that nature offers a plethora of solutions to address this problem, one of which is Black Seed Oil.
Understanding Eczema
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a non-contagious, inflammatory skin condition that can affect individuals from infancy to old age. It’s characterised by dry, cracked, scaly skin, redness, and intense itching. There are several types of eczema, including atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, neurodermatitis, nummular eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and stasis dermatitis.
The most common type is atopic dermatitis, also known as atopic eczema. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis include rashes, redness, scaling, and occasionally small blisters. These patches may appear on various parts of the body depending on the individual’s age. The condition evolves in the form of recurrent inflammatory flare-ups followed by periods of remission.
Eczema can be triggered by various factors such as a weakened or abnormally functioning immune system, other health conditions such as hay fever and asthma, dry skin, insect bites, environmental factors, stress, damp hands and feet, and allergies to chemicals, metals, or certain substances. Over time, the skin can become thickened, bumpy, and constantly itch, even when the inflammation is not present. Diagnosis involves a physical examination and tests to rule out other conditions. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Black Seed Oil as a Potential Remedy for Eczema
Black seed oil is rich in thymoquinone, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound. It also contains other key compounds such as Thymol, Carvacrol, and Lauric acid, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Black seed oil's anti-inflammatory ingredients, especially thymoquinone, target inflammation, offering quick relief. It can soothe skin inflammation and reduce itchiness. Moreover, black seed oil acts as a moisturizer, sealing in hydration and nourishing the skin. Thymoquinone, a compound in black seed oil, plays a significant role in targeting inflammation.
Scientific Evidence
Research suggests that black seed oil could be beneficial for skin conditions such as eczema. Its anti-inflammatory properties can help soothe skin inflammation and reduce itchiness.
In a randomized controlled double-blinded study in 2012, 60 patients were given an ointment with black seed oil. This turned out to be more effective in soothing eczema symptoms compared to a Eucerin ointment.
Black cumin seed oil is considered to have powerful anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties. It can be very helpful for various skin issues like eczema, psoriasis, and even acne.
However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits of black seed oil for these conditions.
How to Use Black Seed Oil for Eczema
While there's no standard dosage for using black seed oil for eczema, it's generally safe to apply it topically on the affected areas. Applying Black Seed Oil for an eczema outbreak can vary depending on unique needs and the severity of symptoms. However, a general guideline is to apply the oil to the affected areas twice to thrice daily.
- Start by cleansing the affected skin gently with a mild, fragrance-free cleanser and patting it dry.
- Then, massage a small amount of Black Seed Oil into the affected areas using gentle, circular motions.
- Allow the oil to sink into the skin before covering the area with loose, breathable clothing.
Individual responses to Black Seed Oil can vary, and some may require more or less frequent applications. Monitoring your skin’s response and adjusting the frequency accordingly is key. It's always best to do a patch test first to check for any allergic reactions.
Here are seven lifestyle tips and tricks for managing skin conditions:
Avoid Scratching: Try your best to resist the urge to scratch or rub your skin. This can lead to thickening of the skin over time.
Maintain Short Nails: Keeping your nails short can help prevent further damage to your skin. If you find it hard to stop scratching, try to keep your hands occupied.
Use Fragrance-Free Laundry Products: When washing your clothes, opt for products that are free of fragrance and avoid using fabric softener.
Choose Breathable Clothing: Opt for clothing that allows your skin to breathe. Cotton is often a good choice for this.
Invest in a Humidifier: If you live in a dry climate, consider investing in a humidifier. Remember to clean it regularly to prevent it from becoming a breeding ground for mould.
Limit Shower Time: Try to reduce your time in the shower and use lukewarm water instead of hot water.
Stay Cool During Exercise: Wear lightweight, breathable clothing when exercising. If you start to feel itchy, use a cooling spray. You might also consider taking a non-sedating antihistamine before you exercise to minimise any skin reaction.
Keep Your Skin Moisturised: Apply a moisturiser immediately after showering to lock in moisture and keep your skin hydrated.